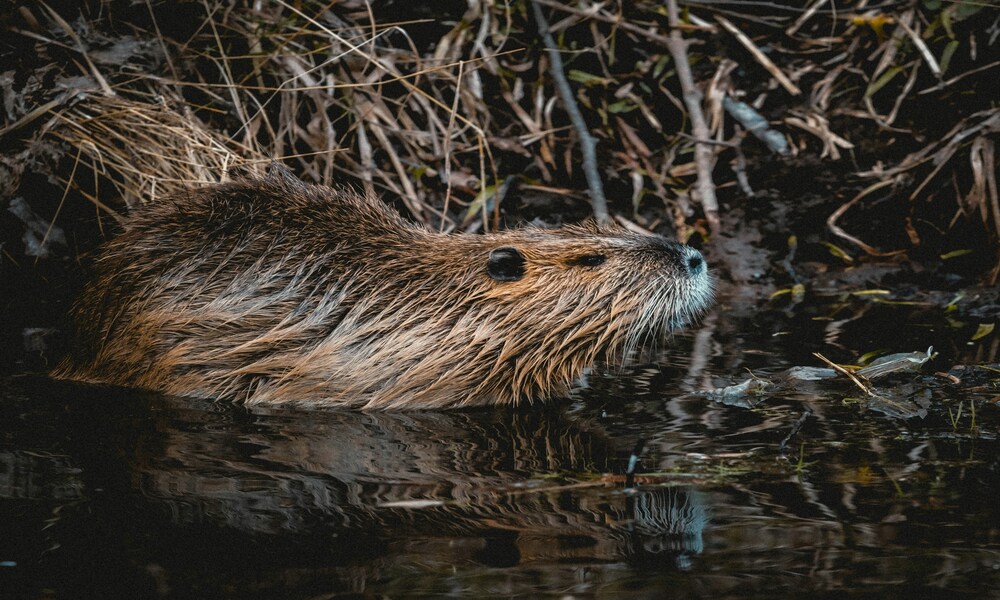
It may be spring now, but our recent winters have been dominated by flooding. Could the return of beavers to farmlands play its part in helping resolve some of these issues? Often called “nature’s engineers”, beavers play a significant role in shaping ecosystems. Their reintroduction to agricultural areas could bring about remarkable ecological benefits and economic opportunities.
Understanding Beaver Ecology and Behaviour
Beavers are known for their ability to create wetlands through the construction of dams, which can have profound environmental effects. Through the building of dams, the digging of canals, and the creation of dead wood, beavers create and maintain habitats where an abundance and diversity of life can flourish. Dams for example prevent soil eroded from fields being washed away into the sea. Carbon and nutrients are trapped, therefore improving water quality downstream. The flow of water is slowed, helping to ameliorate flooding.
Beavers and the landscapes they generate benefit both wildlife and people by:
- Helping to reduce downstream flooding – the channels, dams, and wetland habitats that beavers create hold back water and release it more slowly after heavy rain.
- Increasing water retention.
- Cleaning water.
- Reducing siltation, which pollutes water.
- Creating wetlands which absorb carbon – essential in this climate crisis.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of reintroducing beavers to farms are substantial, this approach is not without its challenges. Beavers can sometimes conflict with agricultural activities, particularly when their dams lead to waterlogging or flooding of crops.
Effective management strategies are essential to mitigate these negative impacts. This may involve creating beaver management plans that include mechanisms for controlling dam height or redirecting water flow.
Additionally, there is a need for ongoing education and community engagement. Farmers and landowners must understand the ecological benefits of beavers and how to coexist with them successfully. Collaboration among agricultural stakeholders, wildlife biologists, and conservation organisations will be crucial in developing strategies that balance the needs of farming with ecological sustainability.